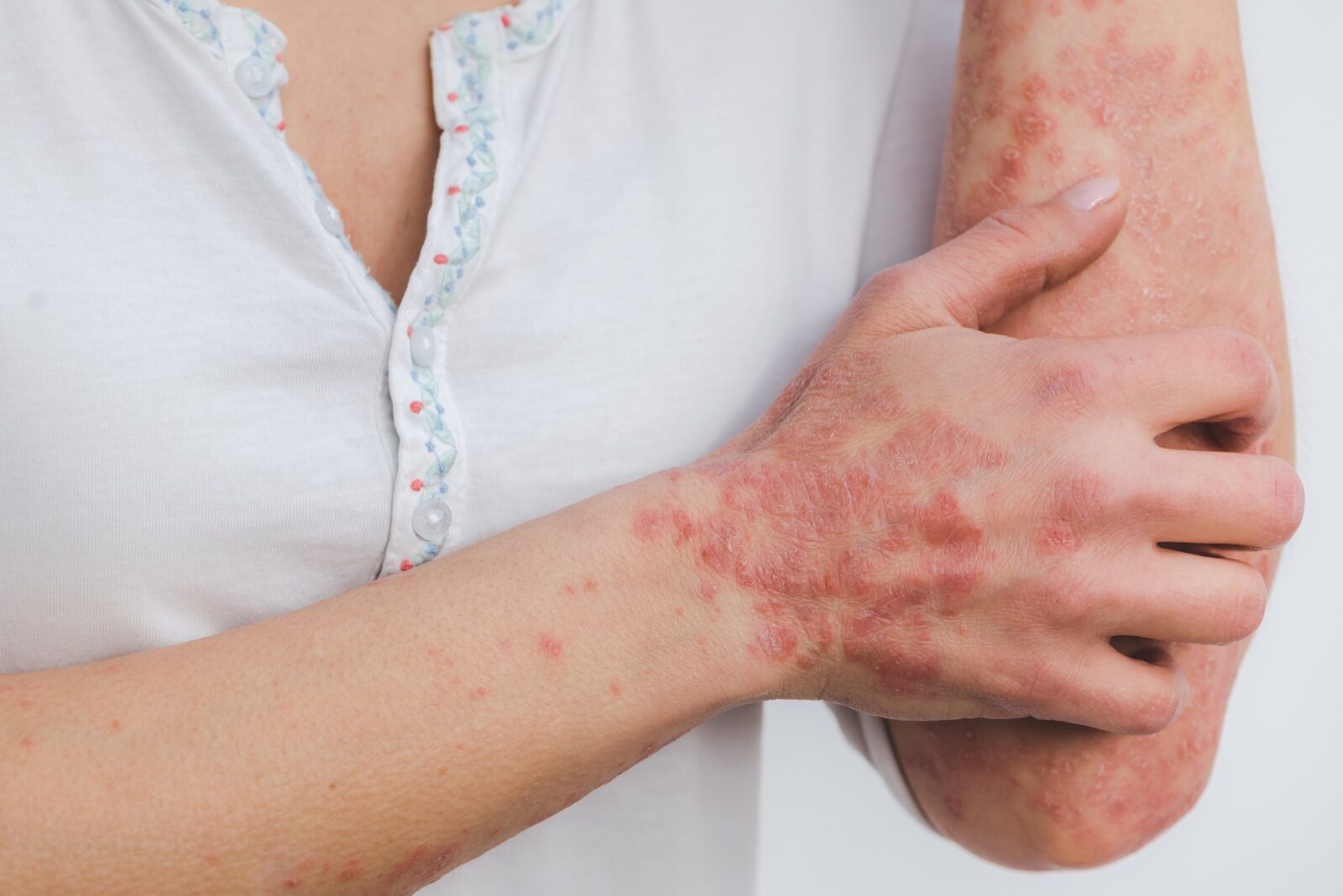
Psoriasis can be very uncomfortable. Certain habits trigger this disease. However, a proper diet can prevent flare-ups.
Change starts with your diet. Nutrition is an essential part of our lives; however, we often don’t think about feeding our bodies with healthy food. Although there is not enough evidence to support this theory, our diet plays a huge role in good health and nutrition.
However, different people require different diets. A low-calorie diet may help obese people reduce psoriasis symptoms. People suffering from both psoriasis and celiac diseases could improve their skin health by avoiding gluten foods. Every diet is different from person to person, and it doesn’t necessarily work for everyone.
What to avoid
Don’t forget that psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease, meaning avoiding or limiting certain foods will help your case. Processed food is bad for everyone in general. Therefore try to avoid sugar, sodium, fats, and other additives found in ultra-processed foods.
Here are a few examples:
- pastries, cookies, and crackers
- ice cream
- candy
- breakfast cereal
- soft drinks
Red meat and dairy can also provoke psoriasis attacks. You should also avoid high-glycemic foods, such as:
- white bread
- bagels
- white rice
Although vegetables are healthy in general, there are few veggies you should reduce from your diet, such as:
- tomatoes
- potatoes (except sweet potatoes)
- eggplant
- peppers
Even certain spices made from peppers can accelerate psoriasis symptoms, such as cayenne and paprika. Another thing you should control is your alcohol intake. An excessive amount of alcohol has a negative effect if you have this condition.
What to eat
Mediterranean diet is one of the best diets and the doctors’ choice. However, one diet doesn’t work for everyone. Try it for a month and see how it goes for you. Here is what you should include in your diet:
- omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, herring, chia seeds
- fruits and vegetables, such as dark, leafy greens, yellow beans, pumpkin
- healthy fats, such as avocado, coconut oil, olives
- high-quality proteins, such as wild fish, beans, lentils
- Vitamin D, such as cod liver oil, salmon, eggs, orange juice



















Leave a Reply